Promotional price valid on web orders only. Your contract pricing may differ. Interested in signing up for a dedicated account number?
Learn More
Learn More
MilliporeSigma™ Aβ-42, oligomeric (VIA), Rabbit, Unlabeled, Polyclonal,
Rabbit Polyclonal Antibody
Supplier: MilliporeSigma™ ABN1650
Description
Amyloid beta A4 protein (UniProt P05067; also known as ABPP, Alzheimer disease amyloid protein, Amyloid precursor protein, APP, APPI, Cerebral vascular amyloid peptide, CVAP, PN-II, PreA4, Protease nexin-II) is encoded by the APP (also known as A4, AD1) gene (Gene ID 351) in human. Amyloid precursor protein (APP) is initially produced with a signal peptide sequence (a.a. 1-17), the removal of which yields the mature protein with a large extracellular portion (a.a. 18-699), followed by a transmembrane segment (a.a. 700-723) and a cytoplasmic (a.a. 724-770) tail. APP can be further processed by the α-, β-, and γ-secretases in two alternative processing pathways. In the non-amyloidogenic pathway, APP is first cleaved by the plasma membrane-localized α-secretase to generate an N-terminal extracellular sAPPα fragment (a.a. 18-687) and a membrane-bound C-terminal fragment C83 (CTFα), which can be further cleaved by γ-secretase to produce a non-toxic small peptide p3 and a cytoplasmic APP intracellular domain (AICD). In the amyloidogenic pathway, APP undergoes β-cleavage in BACE-1 (β-site APP-cleaving enzyme)-enriched endosomes to generate an N-terminal extracellular sAPPβ fragment (a.a. 18-671) and a membrane-bound C-terminal fragment C99 (CTFβ). Subsequent cleavage of C99 by γ-secretase releases the amyloid β peptides, Aβ1-42 (672-713) and Aβ1-40 (672-711), and AICD. Aβ accumulation in the cortical and hippocampal regions of the brain is a major pathological feature of Alzheimer's disease (AD). Growing evidences implicate soluble oligomers as the more toxic species and the extent of oligomer formation and assembly correlates better with disease progression and cognitive dysfunction. These Aβ oligomers are able to induce other aggregation-prone proteins, including α-synuclein (α-syn), prion protein (PrP), and TDP-43, to assume oligomeric conformations. These proteins can then seed tau aggregation, resulting in neurodegeneration.
Specifications
| Aβ-42, oligomeric (VIA) | |
| Polyclonal | |
| Unconjugated | |
| APP, A4, AD1 | |
| Rabbit | |
| Unpurified | |
| RUO | |
| Primary | |
| Human | |
| Serum |
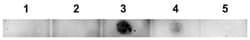
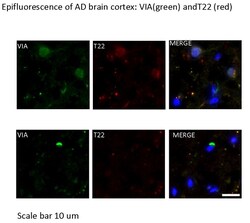
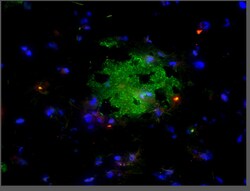
| Immunofluorescence, Immunohistochemistry, Western Blot | |
| Please refer to lot specific datasheet. | |
| Rabbit polyclonal antibody serum with 0.05% Sodium Azide. | |
| P05067 | |
| Aggregated synthetic hexapeptide VIAVIA composed of two copies of Aβ-42 C-terminal end 3-amino acid sequence (Bodani, R.U., et al. (2015). ACS Chem. Neurosci. 6(12):1981-1989). | |
| 100 μL | |
| Neuroscience | |
| This polyclonal antiserum (VIA) recognizes a distinct epitope specific to Aβ-42 oligomers. VIA does not recognize classic amyloid plaques composed of fibrillar Aβ or Aβ-40 (Bodani, R.U., et al. (2015). ACS Chem. Neurosci. 6(12):1981-1989). | |
| Stable for 1 year at -20°C from date of receipt. Handling Recommendations: Upon receipt and prior to removing the cap, centrifuge the vial and gently mix the solution. Aliquot into microcentrifuge tubes and store at -20°C. Avoid repeated freeze/thaw cycles, which may damage IgG and affect product performance. |
Product Content Correction
Your input is important to us. Please complete this form to provide feedback related to the content on this product.
Product Title
For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures.
Spot an opportunity for improvement?Share a Content Correction