Learn More
PMS2 Mouse, Unlabeled, Clone: A16-4, BD
Mouse Monoclonal Antibody
Supplier: BD Biosciences 556415
Description
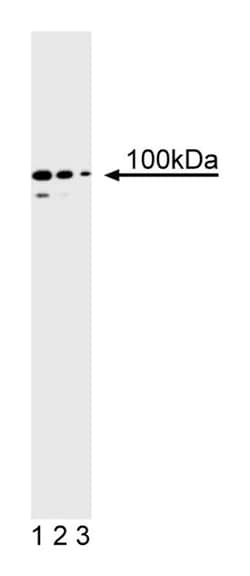
The repair of mismatched DNA is essential to maintaining the integrity of genetic information over time. In bacteria the DNA repair process is accomplished by the MutL, MutH, and MutS proteins. The MutS protein initially recognizes and binds to mismatched DNA. Following this, MutH, an endonuclease, and MutL form a complex with MutS and carry out an excision repair mechanism. When bacteria are deficient in one of these enzymes a mutator phenotype arises characterized by genetic instability. The important role played by DNA repair enzymes is emphasized by the fact that they are highly conserved from bacteria to yeast to mammals. In humans the proteins are called MutS homolog2 (MSH2), MutL homolog (MLH1), and PMS2 which is also a homolog of MutL. After MSH2 and a partner bind to a mismatched DNA duplex, the complex is joined by a heterodimer of MLH1 and PMS2 which together help facilitate the later steps in mismatch repair. Two other members of this family, MSH3 and MSH6, can also join the MSH2-containing complex to help facilitate repair. The reduced molecular weight of PMS2 is ∽100kDa. mAb A16-4 recognizes human and mouse PMS2. Recombinant human PMS2 (C-terminal half) was used as immunogen.
Host Species: Mouse
Clone: A16-4
Isotype: IgG1 κ
Species Reactivity: Human
Immunogen: Recombinant Human PMS2
Immunofluorescence, Immunoprecipitation, Western Blotting

Specifications
| PMS2 | |
| Monoclonal | |
| 0.5mg/mL | |
| Aqueous buffered solution containing ≤0.09% sodium azide. | |
| Recombinant Human PMS2 | |
| 0.1 mg | |
| Cell Biology | |
| Human, Mouse | |
| IgG1 κ |
| Western Blot | |
| A16-4 | |
| Unconjugated | |
| Mouse | |
| Affinity Purified | |
| RUO | |
| Primary | |
| Store undiluted at 4°C |
Safety and Handling
Your input is important to us. Please complete this form to provide feedback related to the content on this product.
For Research Use Only.