Promotional price valid on web orders only. Your contract pricing may differ. Interested in signing up for a dedicated account number?
Learn More
Learn More
MilliporeSigma™ anti-Siglec-1 (CD169) Clone: 5F1.1,
Mouse Monoclonal Antibody
Supplier: MilliporeSigma™ MABT328
Description
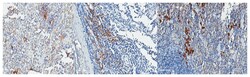
Specifically detects Siglec-1 (CD169) Clone: 5F1.1 in Human, Mouse samples, and it is validated for Immunohistochemistry (Paraffin), Western Blotting
Sialoadhesin (UniProt Q9BZZ2; also known as CD169, Sialic acid-binding Ig-like lectin 1, Sialic acid-binding immunoglobulin-like lectin 1, Siglec-1) is encoded by the SIGLEC1 (also known as SN) gene (Gene ID 6614) in human. Sialoadhesin/CD169/Siglec-1 is the founding member of the sialic acid-binding immunoglobulin lectins (Siglec) expressed on a variety of leukocytes and stromal cells. Sialoadhesin is initially produced with a signal sequence (a.a. 1-19), the removal of which yields the mature protein with a large extracellular portion (a.a. 20-1641), followed by a transmembrane segment (a.a. 1642-1662), and a short cytoplasmic tail (a.a. 1663-1709) with no known signal transduction or endocytosis motifs. The extracellular portion contains an N-terminal Ig-like V-type domain (a.a. 20-136), followed by sixteen Ig-like C2-type domains. Sialoadhesin is highly expressed on the subcapsular sinus (SCS) and medullary macrophages in lymph node (LN) and on marginal metallophilic macrophages in the marginal zone (MZ) of spleen. Although sialic acids are found on the surface of all cells and most secreted proteins, Only heavily sialylated, multimeric structures are captured by Sialoadhesin on macrophages via its N-terminal Ig-like V-type domain due to a low (millimolar) affinity toward sialylic acid. Sialoadhesin-mediated sialic-acid recognition allows macrophages to engage sialylated pathogens and stimulate inflammatory responses. Sialoadhesin is also reported to capture of B cell-derived exosomes via their surface-expressed α2, 3-linked sialic acids. In the lymph node, exosomes are not retained in the subcapsular sinus of Siglec1-knockout mice and penetrate deeper into the paracortex, causing an enhanced response to antigen-pulsed exosomes among Siglec1-/- mice.
Specifications
| Siglec-1 (CD169) | |
| Monoclonal | |
| Unconjugated | |
| Q9BZZ2 | |
| Mouse | |
| Protein G purified | |
| RUO | |
| Primary | |
| Expected to react with all three spliced isoforms of human Siglec-1 (CD169)/Sialoadhesin reported by UniProt (Q9BZZ2). | |
| 2°C to 8°C for one year from date of shipment | |
| IgG2a κ |
| Immunohistochemistry (Paraffin), Western Blot | |
| 5F1.1 | |
| Purified mouse monoclonal IgG2aκ antibody in buffer containing 0.1M Tris-Glycine (pH 7.4), 150mM NaCl with 0.05% sodium azide. | |
| SIGLEC1, SN | |
| GST-tagged recombinant human Siglec-1 (CD169) N-terminal fragment containing the Ig-like V-type domain. | |
| 100 μg | |
| Cell Structure | |
| NP_075556 | |
| Human, Mouse | |
| Purified |
Product Content Correction
Your input is important to us. Please complete this form to provide feedback related to the content on this product.
Product Title
For Research Use Only
Spot an opportunity for improvement?Share a Content Correction