Promotional price valid on web orders only. Your contract pricing may differ. Interested in signing up for a dedicated account number?
Learn More
Learn More
Invitrogen™ CD273 (B7-DC) Polyclonal Antibody
Rabbit Polyclonal Antibody
Supplier: Invitrogen™ PA582484
Description
Immunogen sequence: GYPLAEVSWP NVSVPANTSH SRTPEGLYQV TSVLRLKPPP GRNFSCVFWN THVRELTLAS IDLQSQMEPR THPT.
Programmed death-ligand 2 (PD-L2), or B7-DC, is a member of the B7 ligand family within the immunoglobulin superfamily that, along with programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1), acts as a ligand for programmed cell death protein 1 (PD-1). Though expressed primarily in dendritic cells, PD-L2 expression can be induced on a wide variety of immune and non-immune cells depending on the microenvironment. PD-L2 expression is particularly upregulated in the presence of Th2 cytokine, IL-4, as well as Th1 cytokines, TNF-alpha and IFN-gamma to a lesser degree. While generally expressed at lower levels compared to PD-L1, PD-L2 demonstrates a 2 to 6 times higher relative affinity to PD-1 than PD-L1. PD-1 and its ligands are referred to as inhibitory immune checkpoint molecules in that they provide useful negative feedback during physiological homeostasis. Ligation of PD-L2 or PD-L1 inhibits activation, proliferation, and cytokine secretion (e.g. IFN-gamma, IL-10) in T cells, ultimately dampening immune response. Conversely, studies have shown that PD-L2 can also stimulate T cell proliferation and cytokine production, even in PD-1-deficient T cells, suggesting additional receptors. Recent studies have concluded that PD-L2 also binds to a second receptor, repulsive guidance molecule b (RGMb), which was originally identified as a receptor for bone morphogenetic proteins (BMPs). RGMb is expressed in the central nervous system, as well as in macrophages, however, its role in immunity is only beginning to emerge. Interaction between PD-L2 and RGMb regulates the development of respiratory tolerance in the lung through BMP and/or neogenin signaling pathways. The naturally occurring human PD-L2 monomer consists of a 201-amino-acid extracellular domain, a 21-amino-acid transmembrane domain, and a 32-amino-acid cytoplasmic domain.
Specifications
| CD273 (B7-DC) | |
| Polyclonal | |
| Unconjugated | |
| PDCD1LG2 | |
| B7 dendritic cell molecule; B7DC; B7-DC; bA574F11.2; Btdc; Butyrophilin B7-DC; butyrophilin-like protein; CD273; F730015O22Rik; MGC124039; MGC124040; PD1 ligand 2; PD-1 ligand 2; PD-1-ligand 2; PDCD1 ligand 2; PDCD1L2; Pdcd1lg2; Pdl2; PD-L2; Programmed cell death 1 ligand 2; programmed death ligand 2 | |
| Rabbit | |
| Antigen affinity chromatography | |
| RUO | |
| 80380 | |
| Store at 4°C short term. For long term storage, store at -20°C, avoiding freeze/thaw cycles. | |
| Liquid |
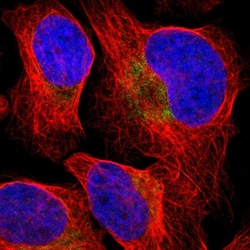
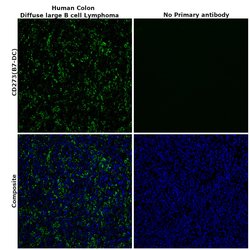
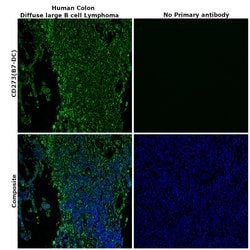
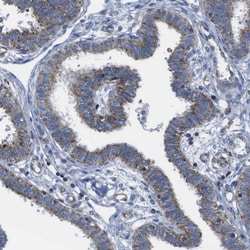
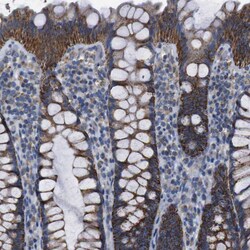
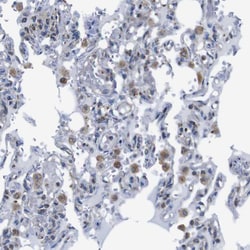
| Immunohistochemistry (Paraffin), Immunocytochemistry, Immunohistochemistry (Paraffin) | |
| 0.3 mg/mL | |
| PBS with 40% glycerol and 0.02% sodium azide; pH 7.2 | |
| Q9BQ51 | |
| PDCD1LG2 | |
| Recombinant protein corresponding to Human PDCD1LG2. Recombinant protein control fragment (Product #RP-90599). | |
| 100 μL | |
| Primary | |
| Human | |
| Antibody | |
| IgG |
Product Content Correction
Your input is important to us. Please complete this form to provide feedback related to the content on this product.
Product Title
Spot an opportunity for improvement?Share a Content Correction