Learn More
Invitrogen™ CD314 (NKG2D) Monoclonal Antibody (C7), Functional Grade, eBioscience™
Armenian Hamster Monoclonal Antibody
$258.00
Specifications
| Antigen | CD314 (NKG2D) |
|---|---|
| Clone | C7 |
| Concentration | 1 mg/mL |
| Content And Storage | 4°C |
| Applications | Flow Cytometry, Functional Assay, Neutralization |
Description
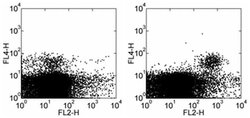
Description: The C7 monoclonal antibody reacts with the mouse NKG2D. NKG2D is a lectin-like molecule expressed on both human and mouse NK cell lineage. mouse NKG2D binds to retinoic acid-inducible RAE1-alpha, -beta, -gamma, -delta, and -ε and the minor histocompatibility molecule H60 and has the ability to costimulate multiple NK activation receptors through the DAP12/DAP10 adaptor molecules. NKG2D is expressed by all spleen and liver NK cells, NK1.1^+ thymocytes, in vitro activated LAK cells and a subset of splenic NKT cells. A10 and C7 antibodies detect NK cells from all inbred strains of mouse tested so far. C7 is reported to interfere with the interaction of NKG2D with its ligands as shown by inhibition of lysis of Ba/F3-RAE1d by C57BL/6 LAK cells in the presence of the C7 mAb. C7 and another hamster anti-mouse NKG2D (clone A10, Product # 14-5872) compete with each other for binding to transfected cells by flow cytometric analysis, suggesting that they may bind to similar epitopes or block each other by steric hindrance. C7 (neutralizing) and A10 (activating) also exhibit different functional properties. Expression of the NKG2D antigen on mouse peripheral NK and NKT cells can be detected by flow cytometric analysis using mAb CX5 with much brighter intensity. Applications Reported: C7 has been reported for use in flow cytometric analysis, and in vitro blocking of mouse NKG2D (blocking). Applications Tested: This C7 antibody has been tested by flow cytometric ana...
Natural killer (NK) cells are lymphocytes that can mediate lysis of certain tumor cells and virus-infected cells without previous activation. NK cells can regulate specific humoral and cell-mediated immunity, and preferentially express several calcium-dependent (C-type) lectins, which have been implicated in the regulation of NK cell function. The NK gene encodes a member of the NKG2 family, and the encoded transmembrane protein is characterized by a type II membrane orientation (extracellular C terminus) and the presence of a C-type lectin domain. The NKG2 gene family is located within the NK complex, a region that contains several C-type lectin genes preferentially expressed in NK cells.Specifications
| CD314 (NKG2D) | |
| 1 mg/mL | |
| Flow Cytometry, Functional Assay, Neutralization | |
| Functional Grade | |
| Armenian Hamster | |
| RUO | |
| PBS with no preservative; pH 7.2 | |
| O54709 | |
| 27007 | |
| Primary | |
| Affinity chromatography |
| C7 | |
| 4°C | |
| Monoclonal | |
| Liquid | |
| IgG | |
| Mouse | |
| Klrk1 | |
| CD314; D12S2489E; D6H12S2489E; killer cell lectin like receptor K1; Killer cell lectin-like receptor subfamily K member 1; killer cell lectin-like receptor subfamily K, member 1; KLR; Klrk1; natural killer cell group 2D; natural killer cell receptor; NK cell receptor D; NK lectin-like receptor; Nkg2d; NKG2-D; NKG2-D type II integral membrane protein; NKG2-D-activating NK receptor; NKLLR; Nkrp2; NKR-P2; NKR-P2, ortholog of human NKG2D | |
| Klrk1 | |
| Antibody |
The Fisher Scientific Encompass Program offers items which are not part of our distribution portfolio. These products typically do not have pictures or detailed descriptions. However, we are committed to improving your shopping experience. Please use the form below to provide feedback related to the content on this product.