Learn More
Invitrogen™ Cyclin D1 Polyclonal Antibody
Rabbit Polyclonal Antibody
Supplier: Invitrogen™ PA585257
Description
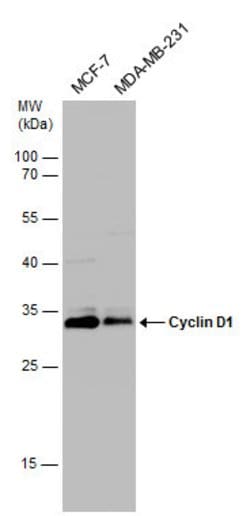
Keep as concentrated solution. Predicted reactivity: Mouse (93%), Rat (93%), Xenopus laevis (80%), Dog (94%), Chicken (86%), Rhesus Monkey (99%), Bovine (93%). Positive Control: HeLa, MCF-7, MDA-MB-231, Huh 7, H184B5F5/M10, BT-474, HCC1937, Hs578T, MDA-MB-231, MDA-MB-361, MDA-MB-453, T47D, ZR-75-1. Store product as a concentrated solution. Centrifuge briefly prior to opening the vial.
Cyclin D1 (PRAD-1, bcl-1) is one of the key cell cycle regulators, and functions in association with cdk4 and/or cdk6 by phosphorylating the Rb protein. Cyclin D1 is a putative proto-oncogene overexpressed in a wide variety of human neoplasms including mantle cell lymphomas (MCL). In addition, cyclin D1 positively regulates protein phosphorylation, mammary gland epithelial cell proliferation, and fat cell differentiation. In humans, the CCND1 gene encoding cyclin D1 is present on chromosome 11. Cyclin D1 is a cytoplasmic and nuclear protein that is synthesized during G1 phase and assembles with either cyclin-dependent kinase 4 (CDK4) or CDK6 in response to growth factor stimulation. D-type cyclin-CDK complexes act to inactivate the growth-suppressive function of the Rb protein through its phosphorylation, and titrate CDK inhibitors such as p21Cip1 and p27Kip1. Without growth factor-mediated stimulation, Cyclin D1 is unstable, and undergoes ubiquitin-mediated degradation, which is triggered by its phosphorylation. Cyclin D1 destabilization participates in G1/S phase arrest. The Cyclin D1 protein belongs to the highly conserved cyclin family, whose members are characterized by a dramatic periodicity in protein abundance throughout the cell cycle. Cyclins function as regulators of CDK kinases. Different cyclins exhibit distinct expression and degradation patterns which contribute to the temporal coordination of each mitotic event. Cyclin D1 forms a complex with and functions as a regulatory subunit of CDK4 or CDK6, whose activity is required for cell cycle G1/S transition. The Cyclin D1 protein has been shown to interact with tumor suppressor protein Rb and the expression of this gene is regulated positively by Rb. Mutations, amplification and overexpression of this gene, which alters cell cycle progression, are observed frequently in a variety of tumors and may contribute to tumorigenesis. Cyclin D1 has been successfully employed and is a promising tool for further studies in both cell cycle biology and cancer associated abnormalities.
Specifications
| Cyclin D1 | |
| Polyclonal | |
| Unconjugated | |
| CCND1 | |
| AI327039; B-cell CLL/lymphoma 1; B-cell lymphoma 1 protein; BCL1; BCL-1; BCL-1 oncogene; CCND1; CCND1 protein; cD1; cDNA; CycD1; cyclin D1; Cyl-1; D11S287E; FLJ93625; G1/S-specific cyclin-D1; mRNA; PRAD1; PRAD-1; PRAD1 oncogene; U21B31 | |
| Rabbit | |
| Antigen Affinity Chromatography | |
| RUO | |
| 58919, 595 | |
| Store at 4°C short term. For long term storage, store at -20°C, avoiding freeze/thaw cycles. | |
| Liquid |
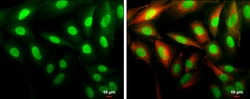
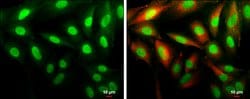
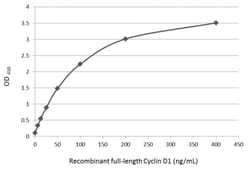
| ELISA, Immunoprecipitation, Western Blot, Immunocytochemistry | |
| 1.21 mg/mL | |
| PBS with 20% glycerol and 0.025% ProClin 300; pH 7 | |
| P24385, P39948 | |
| CCND1 | |
| Full length human Cyclin D1 Recombinant protein. | |
| 100 μL | |
| Primary | |
| Human, Rat | |
| Antibody | |
| IgG |
Your input is important to us. Please complete this form to provide feedback related to the content on this product.