Learn More
Invitrogen™ E4BP4 (NFIL3) Monoclonal Antibody (S2M-E19), PE, eBioscience™
Rat Monoclonal Antibody
Supplier: Invitrogen™ 12592780

Description
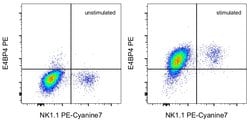
Description: This S2M-E19 monoclonal antibody recognizes mouse E4BP4 (NFIL3), a basic leucine zipper transcription factor first identified for its binding to the promoters of the adenovirus E4 protein and human IL-3. E4BP4 is involved in the transcriptional control of the mammalian circadian clock, motor neuron growth and survival, regulation of von Willbrand factor expression, and osteoblast function. In addition, it is also required for the development of NK and NKT cells as well as CD8a+ dendritic cells. Although relatively high levels of mRNA are reported in resting NK and NKT cells, studies at eBioscience have observed expression of E4BP4 protein in lymphocytes only after activation. Applications Reported: This S2M-E19 antibody has been reported for use in intracellular staining followed by flow cytometric analysis. Applications Tested: This S2M-E19 antibody has been tested by intracellular staining and flow cytometric analysis of stimulated mouse splenoyctes using the Foxp3/Transcription Factor Staining Buffer Set (Product # 00-5523-00) and protocol. This can be used at less than or equal to 0.25 μg per test. A test is defined as the amount (μg) of antibody that will stain a cell sample in a final volume of 100 μL. Cell number should be determined empirically but can range from 10^5 to 10^8 cells/test. It is recommended that the antibody be carefully titrated for optimal performance in the assay of interest. Excitation: 488-561 nm; Emission: 578 nm; Laser: B...
Expression of interleukin-3 (IL3; MIM 147740) is restricted to activated T cells, natural killer (NK) cells, and mast cell lines. Transcription initiation depends on the activating capacity of specific protein factors, such as NFIL3, that bind to regulatory regions of the gene, usually upstream of the transcription start site (Zhang et al., 1995 [PubMed 7565758]).
Specifications
| E4BP4 (NFIL3) | |
| Monoclonal | |
| 0.2 mg/mL | |
| PBS with 0.09% sodium azide; pH 7.2 | |
| O08750 | |
| NFIL3 | |
| Affinity chromatography | |
| RUO | |
| 18030 | |
| 4°C, store in dark, DO NOT FREEZE! | |
| Liquid |
| Flow Cytometry | |
| S2M-E19 | |
| PE | |
| NFIL3 | |
| AV225605; E4 promoter binding-protein 4; E4 promoter-binding protein 4; E4BP4; Embryo implantation-related NFIL3/E4BP4-like transcription factor; IL3BP1; Interleukin-3 promoter transcriptional activator; interleukin-3-binding protein 1; NF IL3A; NFIL3; NFIL3A; NF-IL3A; nuclear factor interleukin 3 regulated protein; nuclear factor interleukin-3-regulated protein; nuclear factor, interleukin 3 regulated; nuclear factor, interleukin 3, regulated; OTTHUMP00000021633; transcriptional activator NF-IL3A | |
| Rat | |
| 25 μg | |
| Primary | |
| Mouse | |
| Antibody | |
| IgG2a κ |
Safety and Handling
The Fisher Scientific Encompass Program offers items which are not part of our distribution portfolio. These products typically do not have pictures or detailed descriptions. However, we are committed to improving your shopping experience. Please use the form below to provide feedback related to the content on this product.