Promotional price valid on web orders only. Your contract pricing may differ. Interested in signing up for a dedicated account number?
Learn More
Learn More
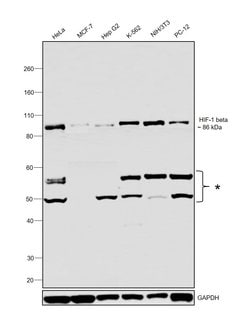
Invitrogen™ HIF-1 beta Monoclonal Antibody (H1beta234)


Mouse Monoclonal Antibody
Supplier: Invitrogen™ MA116512
Description
Suggested positive control: antigen standard for ARNT (transient overexpression lysate).
HIF-1 beta is a series of aryl hydrocarbon receptor nuclear translocator (ARNT) gene products. Hypoxia contributes significantly to the pathophysiology of major categories of human disease, including myocardial and cerebral ischemia, cancer, pulmonary hypertension, congenital heart disease and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Hypoxia contributes significantly to the pathophysiology of major categories of human disease, including myocardial and cerebral ischemia, cancer, pulmonary hypertension, congenital heart disease and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. HIF-1 is a nuclear protein involved in mammalian oxygen homeostasis. This occurs as a posttranslational modification by prolyl hydroxylation. HIF-1 is a heterodimer composed of HIF-1 alpha and HIF-1 beta subunits. Both subunits are constantly translated. However, under normoxic conditions, human HIF-1 alpha is hydroxylated at Pro402 or Pro564 by a set of HIF prolyl hydroxylases, is polyubiquinated, and eventually degraded in proteosomes. Under hypoxic conditions, the lack of hydroxylation prevents HIF degradation and increases transcriptional activity. Therefore, the concentration of HIF-1 alpha increases in the cell. In contrast, HIF-1 beta remains stable under either condition. HIF-1 beta is a series of aryl hydrocarbon receptor nuclear translocator (ARNT) gene products. Diseases associated with HIF-1 beta dysfunction include hypoxia and renal cell carcinoma.HIF-1 beta is a series of aryl hydrocarbon receptor nuclear translocator (ARNT) gene products. Hypoxia contributes significantly to the pathophysiology of major categories of human disease, including myocardial and cerebral ischemia, cancer, pulmonary hypertension, congenital heart disease and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Hypoxia contributes significantly to the pathophysiology of major categories of human disease, including myocardial and cerebral ischemia, cancer, pulmonary hypertension, congenital heart disease and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. HIF-1 is a nuclear protein involved in mammalian oxygen homeostasis. This occurs as a posttranslational modification by prolyl hydroxylation. HIF-1 is a heterodimer composed of HIF-1 alpha and HIF-1 beta subunits. Both subunits are constantly translated. However, under normoxic conditions, human HIF-1 alpha is hydroxylated at Pro402 or Pro564 by a set of HIF prolyl hydroxylases, is polyubiquinated, and eventually degraded in proteosomes. Under hypoxic conditions, the lack of hydroxylation prevents HIF degradation and increases transcriptional activity. Therefore, the concentration of HIF-1 alpha increases in the cell. In contrast, HIF-1 beta remains stable under either condition. HIF-1 beta is a series of aryl hydrocarbon receptor nuclear translocator (ARNT) gene products. Diseases associated with HIF-1 beta dysfunction include hypoxia and renal cell carcinoma.
Specifications
| HIF-1 beta | |
| Monoclonal | |
| 1 mg/mL | |
| PBS with 0.05% sodium azide | |
| P27540, P41739, P53762, Q9BE97 | |
| ARNT | |
| Fusion protein containing amino acids 496-789 of human HIF-1 beta. | |
| 100 μL | |
| Primary | |
| Human, Mouse, Rat, Monkey, Bovine, Sheep, Ferret | |
| Antibody | |
| IgG1 κ |
| ChIP Assay, ChIP sequencing (ChIP-seq), Immunohistochemistry (Paraffin), Immunoprecipitation, Western Blot, Immunocytochemistry | |
| H1beta234 | |
| Unconjugated | |
| ARNT | |
| AHA-1; ARNT; ARNT protein; Arnt1; ARNT1a; ARNT1b; aryl hydrocarbon receptor nuclear translocater; Aryl hydrocarbon receptor nuclear translocator; Aryl hydrocarbon receptor nuclear translocator 1; aryl hydrocarbon receptor nuclear translocator type 1a; aryl hydrocarbon receptor nuclear translocator type 1b; bHLHe2; Class E basic helix-loop-helix protein 2; D3Ertd557e; dioxin receptor, nuclear translocator; Drnt; ESTM42; hif 1; HIF1 beta; HIF-1 beta; Hif1b; HIF1BETA; HIF-1beta; HIF-1-beta; HIF1-beta; hypoxia-inducible factor 1 beta; hypoxia-inducible factor 1, beta subunit; hypoxia-inducible factor 1-beta; mKIAA4051; TANGO; W08714; zgc:136664 | |
| Mouse | |
| Protein G | |
| RUO | |
| 11863, 25242, 281010, 405, 443285 | |
| -20°C, Avoid Freeze/Thaw Cycles | |
| Liquid |
Product Content Correction
Your input is important to us. Please complete this form to provide feedback related to the content on this product.
Product Title
Spot an opportunity for improvement?Share a Content Correction