Learn More
Invitrogen™ HIF-1 beta Recombinant Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody (3R0Y4)
Rabbit Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody
Supplier: Invitrogen™ MA535289
Description
Immunogen sequence: LAPRQQQQQT ELDMVPGRDG LASYNHSQVV QPVTTTGPEH SKPLEKSDGL FAQDRDPRFS EIYHNINADQ SKGISSSTVP ATQQLFSQGN TFPPTPRPAE NFRNSGLAPP VTIVQPSASA GQMLAQISRH SNPTQGATPT WTPTTRSGFS AQQVATQATA KTRTSQFGVG SFQTPSSFSS MSLPGAPTAS PGAAAYPSLT NRGSNFAPET GQTAGQFQTR TAEGVGVWPQ WQGQQPHHRS SSSEQHVQQP PAQQPGQPEV FQEMLSMLGD QSNSYNNEEF PDLTMFPPFS E.
HIF-1 beta is a series of aryl hydrocarbon receptor nuclear translocator (ARNT) gene products. Hypoxia contributes significantly to the pathophysiology of major categories of human disease, including myocardial and cerebral ischemia, cancer, pulmonary hypertension, congenital heart disease and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Hypoxia contributes significantly to the pathophysiology of major categories of human disease, including myocardial and cerebral ischemia, cancer, pulmonary hypertension, congenital heart disease and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. HIF-1 is a nuclear protein involved in mammalian oxygen homeostasis. This occurs as a posttranslational modification by prolyl hydroxylation. HIF-1 is a heterodimer composed of HIF-1 alpha and HIF-1 beta subunits. Both subunits are constantly translated. However, under normoxic conditions, human HIF-1 alpha is hydroxylated at Pro402 or Pro564 by a set of HIF prolyl hydroxylases, is polyubiquinated, and eventually degraded in proteosomes. Under hypoxic conditions, the lack of hydroxylation prevents HIF degradation and increases transcriptional activity. Therefore, the concentration of HIF-1 alpha increases in the cell. In contrast, HIF-1 beta remains stable under either condition. HIF-1 beta is a series of aryl hydrocarbon receptor nuclear translocator (ARNT) gene products. Diseases associated with HIF-1 beta dysfunction include hypoxia and renal cell carcinoma.HIF-1 beta is a series of aryl hydrocarbon receptor nuclear translocator (ARNT) gene products. Hypoxia contributes significantly to the pathophysiology of major categories of human disease, including myocardial and cerebral ischemia, cancer, pulmonary hypertension, congenital heart disease and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Hypoxia contributes significantly to the pathophysiology of major categories of human disease, including myocardial and cerebral ischemia, cancer, pulmonary hypertension, congenital heart disease and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. HIF-1 is a nuclear protein involved in mammalian oxygen homeostasis. This occurs as a posttranslational modification by prolyl hydroxylation. HIF-1 is a heterodimer composed of HIF-1 alpha and HIF-1 beta subunits. Both subunits are constantly translated. However, under normoxic conditions, human HIF-1 alpha is hydroxylated at Pro402 or Pro564 by a set of HIF prolyl hydroxylases, is polyubiquinated, and eventually degraded in proteosomes. Under hypoxic conditions, the lack of hydroxylation prevents HIF degradation and increases transcriptional activity. Therefore, the concentration of HIF-1 alpha increases in the cell. In contrast, HIF-1 beta remains stable under either condition. HIF-1 beta is a series of aryl hydrocarbon receptor nuclear translocator (ARNT) gene products. Diseases associated with HIF-1 beta dysfunction include hypoxia and renal cell carcinoma.
Specifications
| HIF-1 beta | |
| Recombinant Monoclonal | |
| 1.33 mg/mL | |
| PBS with 0.05% BSA, 50% glycerol and 0.02% sodium azide; pH 7.3 | |
| P27540 | |
| ARNT | |
| Recombinant fusion protein containing a sequence corresponding to amino acids 499-789 of human HIF-1 beta (P27540). | |
| 100 μL | |
| Primary | |
| Human | |
| Antibody | |
| IgG |
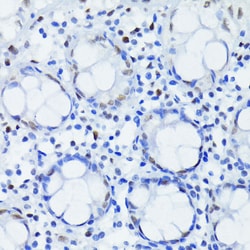
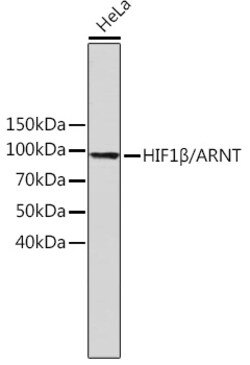
| ELISA, Immunohistochemistry (Paraffin), Western Blot | |
| 3R0Y4 | |
| Unconjugated | |
| ARNT | |
| AHA-1; ARNT; ARNT protein; Arnt1; ARNT1a; ARNT1b; aryl hydrocarbon receptor nuclear translocater; Aryl hydrocarbon receptor nuclear translocator; Aryl hydrocarbon receptor nuclear translocator 1; aryl hydrocarbon receptor nuclear translocator type 1a; aryl hydrocarbon receptor nuclear translocator type 1b; bHLHe2; Class E basic helix-loop-helix protein 2; D3Ertd557e; dioxin receptor, nuclear translocator; Drnt; ESTM42; hif 1; HIF1 beta; HIF-1 beta; Hif1b; HIF1BETA; HIF-1beta; HIF-1-beta; HIF1-beta; hypoxia-inducible factor 1 beta; hypoxia-inducible factor 1, beta subunit; hypoxia-inducible factor 1-beta; mKIAA4051; TANGO; W08714; zgc:136664 | |
| Rabbit | |
| Affinity chromatography | |
| RUO | |
| 405 | |
| -20°C, Avoid Freeze/Thaw Cycles | |
| Liquid |
Your input is important to us. Please complete this form to provide feedback related to the content on this product.