Learn More
Invitrogen™ NOTCH1 Monoclonal Antibody (mN1A), eBioscience™
Mouse Monoclonal Antibody
Supplier: Invitrogen™ 14578581

Description
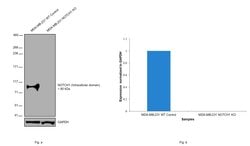
Description: The Notch family of transmembrane receptors controls cell-fate decisions during the development of many organs in a wide variety of species. After binding its ligand, the Notch receptor is cleaved in its transmembrane domain, and the resulting intracellular domain dissociates from the membrane and translocates to the nucleus, where it is able to suppress the expression of lineage-specific genes by interacting with transcriptional repressors. The mN1A antibody reacts with the intracellular domain of mouse and human Notch1, but not with Notch2, 3, or 4. The mN1A antibody has a low affinity for the full-length (unprocessed or heterodimeric cell surface) forms of Notch1. In the mouse, Notch mRNA is expressed in mouse hematopoietic cells of the fetal liver and adult thymus and bone marrow. In the thymus, Notch1 protein is detected in CD4-CD8- (double-negative) and CD4-CD8+ (single-positive) thymocytes. Studies of Notch1-transgenic cells and Notch1-null mice indicate that the receptor is involved in the regulation of lymphopoiesis and myelopoiesis. Applications Reported: This mN1A antibody has been reported for use in intracellular staining followed by flow cytometric analysis, immunoblotting (WB), and immunohistochemical staining. (Fluorochrome conjugated mN1A is recommended for use in intracellular flow cytometry.). Applications Tested: This mN1A antibody has been tested by intracellular staining and flow cytometric analysis of mouse thymocytes. This can be used a...
The notch gene belongs to a family of epidermal growth factor (EGF) like homeotic genes, which encode transmembrane proteins with a variable number of cysteine-rich EGF-like repeats in the extracellular region. Four notch genes have been described in mammals: Notch1, Notch2, Notch3 and Notch4(Int-3), which have been implicated in the differentiation of the nervous system and other structures. The EGF-like proteins Delta and Serrate have been identified as ligands of Notch1. Mature Notch proteins are heterodimeric receptors derived from the cleavage of Notch pre-proteins into an extracellular subunit (NEC) containing multiple EGF-like repeats and a transmembrane subunit including intracellular region (Ntm).
Specifications
| NOTCH1 | |
| Monoclonal | |
| 0.5 mg/mL | |
| PBS with 0.09% sodium azide; pH 7.2 | |
| P46531, Q01705 | |
| Notch1 | |
| Affinity chromatography | |
| RUO | |
| 18128, 4851 | |
| 4°C | |
| Liquid |
| Flow Cytometry, Immunohistochemistry, Western Blot | |
| mN1A | |
| Unconjugated | |
| Notch1 | |
| 9930111A19Rik; AOS5; AOVD1; Drosophila Notch homolog 1 (controlling the the ectodermal and neural cell fate in Drosophila); hN1; lin-12; major type A protein; Mis6; Motch; Motch A; mT14; N1; neurogenic locus notch homolog protein 1; NEXT; NICD; NOTCH; notch 1; Notch 1 extracellular truncation; Notch 1 intracellular domain; Notch gene homolog 1; Notch homolog 1, translocation-associated; notch receptor 1; Notch1; p300; RP23-306D20.12; RP23-306D20.12-001; Tan1; Translocation-associated notch protein TAN-1; transmembrane receptor Notch1 | |
| Mouse | |
| 50 μg | |
| Primary | |
| Human, Mouse | |
| Antibody | |
| IgG1 κ |
The Fisher Scientific Encompass Program offers items which are not part of our distribution portfolio. These products typically do not have pictures or detailed descriptions. However, we are committed to improving your shopping experience. Please use the form below to provide feedback related to the content on this product.