Promotional price valid on web orders only. Your contract pricing may differ. Interested in signing up for a dedicated account number?
Learn More
Learn More
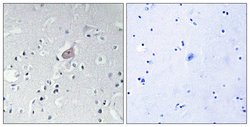
Phospho-c-Abl (Tyr393, Tyr412) Polyclonal Antibody, Invitrogen™
Rabbit Polyclonal Antibody
Supplier: Thermo Scientific PA539687
Description
c-Abl (Abelson murine leukemia viral oncogene homolog 1, ABL1) is a 140 kDa proto-oncogene member of the Src family of non-receptor tyrosine kinases. c-Abl has been implicated in processes of cell differentiation, cell division, cell adhesion, and stress response. Activity of c-Abl protein is negatively regulated by its SH3 domain, and deletion of the SH3 domain turns c-Abl into an oncogene. The t(9;22) translocation results in the head-to-tail fusion of the BCR and c-Abl genes present in many cases of chronic myelogeneous leukemia. The DNA-binding activity of the ubiquitously expressed ABL1 tyrosine kinase is regulated by CDC2-mediated phosphorylation, suggesting a cell cycle function for c-Abl. In chronic myelogenous leukemia and a subset of acute lymphoblastic leukemias, the c-Abl proto oncogene undergoes a (9;22) chromosomal translocation producing a novel rearranged chromosome (the Philadelphia chromosome) As the result of the fusion of c-Abl sequences from chromosome 9 to the Bcr gene on chromosome 22. The molecular consequence of this translocation is the generation of a chimeric Bcr/Abl mRNA encoding activated Abl protein tyrosine kinase. The c-Abl oncogene was initially identified as the viral transforming gene of Abelson murine leukemia virus (A-MuLV). The major translational product of c-Abl has been identified as a protein with tyrosine kinase activity and an SH2 domain. The c-Abl oncogene is implicated in several human leukemias including 90-95% of chronic myelocytic leukemia (CML), 20-25% of adult acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) and 2-5% of pediatric ALL. c-Abl localizes to dynamic actin structures, and phosphorylates CRK and CRKL, DOK1, and other proteins controlling cytoskeleton dynamics. c-ABL potentially regulates DNA repair by activating the proapoptotic pathway when the DNA damage is too severe to be repaired.
Specifications
| Phospho-c-Abl (Tyr393, Tyr412) | |
| Polyclonal | |
| Unconjugated | |
| ABL1 | |
| ABL1, ABL2, ABL, JTK7, p150, Proto-oncogene c-Abl, Tyrosine-protein kinase ABL1, c-Abl, Abelson tyrosine-protein kinase 2, Abelson murine leukemia viral oncogene homolog 2, Abelson-related gene protein, Tyrosine-protein kinase ARG, ABLL, ARG | |
| Rabbit | |
| Antigen affinity chromatography | |
| RUO | |
| 11350, 25, 311860 | |
| -20°C | |
| Liquid |
| Immunocytochemistry, Immunofluorescence, Immunohistochemistry (Paraffin), Western Blot | |
| 1 mg/mL | |
| Dulbecco′s PBS with 150mM NaCl, 50% glycerol and 0.02% sodium azide; pH 7.4 | |
| P00519, P00520 | |
| ABL1 | |
| A synthetic phosphopeptide derived from human Abl around the phosphorylation site of Tyr393/412 (D-T-YP-T-A) | |
| 100 μg | |
| Primary | |
| Human, Mouse, Rat | |
| Antibody | |
| IgG |
Product Content Correction
Your input is important to us. Please complete this form to provide feedback related to the content on this product.
Product Title
Spot an opportunity for improvement?Share a Content Correction