Learn More
Invitrogen™ Phospho-IkB alpha (Ser32) Recombinant Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody (6H4L6)
Rabbit Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody
Supplier: Invitrogen™ 701271
Description
This antibody is predicted to react with equine, rabbit and non-human primate based on sequence homology. Intact IgG appears on a non-reducing gel as ~150 kDa band and upon reduction generating a ~25 kDa light chain band and a ~50 kDa heavy chain. Recombinant rabbit monoclonal antibodies are produced using in vitro expression systems. The expression systems are developed by cloning in the specific antibody DNA sequences from immunoreactive rabbits. Then, individual clones are screened to select the best candidates for production. The advantages of using recombinant rabbit monoclonal antibodies include: better specificity and sensitivity, lot-to-lot consistency, animal origin-free formulations, and broader immunoreactivity to diverse targets due to larger rabbit immune repertoire.
IkB-alpha is a 40 kDa protein that functions to inhibit NF- kappaB activity. The inhibition occurs via protein-protein interaction between I kappaB proteins and NF- kappaB dimers in the cytosol. The interaction of I kappa B-alpha with NF- kappaB masks the nuclear localization sequence of NF- kappaB, preventing NF- kappaB translocation to the nucleus. A variety of stimuli can activate gene expression by liberating NF- kappaB through the degradation of I kappaB alpha. These stimuli include the proinflammatory cytokines TNF- alpha and IL-1 beta, chemokines, PMA, growth factors, LPS, UV irradiation, viral infection, as well as various chemical and physical stresses. In humans, the gene is located on the q arm of chromosome 14. Activation of NFkB requires that IkB be phosphorylated on specific serine residues, which results in targeted degradation of IkB. IkB kinase alpha (IKK alpha), previously designated CHUK, interacts with IkB-alpha and specifically phosphorylates IkB-alpha on the sites that trigger its degradation Serines 32 and 36. IKK alpha appears to be critical for NFkB activation in response to proinflammatory cytokines. Phosphorylation of IkB by IKK alpha is stimulated by the NFkB inducing kinase (NIK), which itself is a central regulator for NFkB activation in response to TNF and IL-1. The functional IKK complex contains three subunits, IKK alpha, IKK beta and IKK gamma, and each appear to make essential contributions to IkB phosphorylation.
Specifications
| Phospho-IkB alpha (Ser32) | |
| Recombinant Monoclonal | |
| 0.5 mg/mL | |
| PBS with 0.09% sodium azide | |
| P25963 | |
| NFKBIA | |
| Phosphopeptide corresponding to amino acids 27-36 of human I K B-Alpha [pS32]. | |
| 100 μg | |
| Primary | |
| Human | |
| Antibody | |
| IgG |
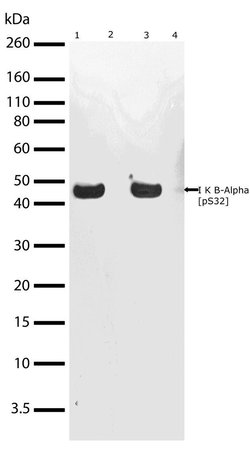
| Western Blot | |
| 6H4L6 | |
| Unconjugated | |
| NFKBIA | |
| AI462015; ECI-6; ECI-6/IKBA; I kappa B-alpha; I(Kappa)B(alpha); I79_018146; IkappaB alpha; IkappaBalpha; I-kappaBalpha; I-kappa-B-alpha; Ikba; IKBalpha; IKB-alpha; Inhibitor of nuclear factor of kappa light chain gene enhancer in B-cells alpha; Inhibitor of nuclear factor of kappa light chain gene enhancer in B-cells, alpha; MAD3; MAD-3; Major histocompatibility complex enhancer-binding protein MAD3; NF kappa B inhibitor alpha; NF-kappaB inhibitor alpha; NF-kappa-B inhibitor alpha; NFKB inhibitor alpha; NFKBI; Nfkbia; nuclear factor of kappa light chain gene enhancer in B-cells; nuclear factor of kappa light chain gene enhancer in B-cells inhibitor, alpha; nuclear factor of kappa light polyp gene enhancer in B-cell 1; nuclear factor of kappa light polypeptide gene enhancer in B cells inhibitor, alpha; nuclear factor of kappa light polypeptide gene enhancer in B-cells inhibitor, alpha; Rel-associated pp40; REL-associated protein pp40; RL/IF-1 | |
| Rabbit | |
| Protein A | |
| RUO | |
| 4792 | |
| Store at 4°C short term. For long term storage, store at -20°C, avoiding freeze/thaw cycles. | |
| Liquid |
Your input is important to us. Please complete this form to provide feedback related to the content on this product.