Promotional price valid on web orders only. Your contract pricing may differ. Interested in signing up for a dedicated account number?
Learn More
Learn More
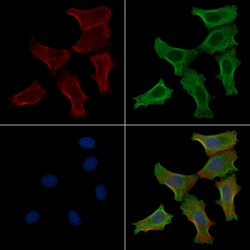
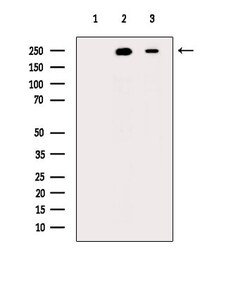
Invitrogen™ Phospho-MYH9 (Ser1943) Polyclonal Antibody
Rabbit Polyclonal Antibody
Supplier: Invitrogen™ PA5105166
Description
Antibody detects endogenous levels of MYH9 only when phosphorylated at Ser1943.
The MYH9 gene, located on chromosome 22q12.3, encodes the heavy chain of non-muscle myosin IIA (NMHC IIA), a critical component of the actin cytoskeleton that plays essential roles in various cellular processes. Structurally, the MYH9 gene spans over 106 kilobases and includes 41 exons that translate into a protein of 1,960 amino acids. This protein is a part of a hexameric complex, which includes two heavy chains, two regulatory light chains, and two essential light chains. The NMHC IIA protein interacts with actin filaments and is involved in cellular activities such as cell migration, adhesion, division, and maintenance of cell shape. Functionally, mutations in MYH9 can result in a spectrum of autosomal dominant disorders collectively known as MYH9-related diseases (MYH9-RD), which include conditions such as May-Hegglin anomaly, Fechtner syndrome, and Epstein syndrome. These disorders are primarily characterized by macrothrombocytopenia (abnormally large platelets) and may lead to other complications such as hearing loss, renal failure, and cataracts later in life. MYH9 is also crucial in hematopoiesis, where its proper function is necessary for the survival and maintenance of hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells (HSPCs). Loss of MYH9 function disrupts normal hematopoiesis, leading to severe blood cell deficiencies and bone marrow failure.
Specifications
| Phospho-MYH9 (Ser1943) | |
| Polyclonal | |
| Unconjugated | |
| MYH9 | |
| BDPLT6; Cellular myosin heavy chain, type A; DFNA17; epsts; fi22c04; fj85e11; flectin; Fltn; FTNS; KLG/PTK7; LOC100911597; LOW QUALITY PROTEIN: myosin-9; MGC104539; MHA; Myh9; myh9.L; myh9a; myh9l2; Myhn1; Myhn-1; myosin; Myosin Heavy Chain 2A; myosin heavy chain 9; myosin heavy chain IX; myosin heavy chain, non-muscle IIa; myosin IIA; myosin, heavy chain 9, non-muscle; myosin, heavy chain 9, non-muscle L homeolog; myosin, heavy chain 9, non-muscle, like-2; myosin, heavy chain 9a, non-muscle; myosin, heavy polypeptide 9, non-muscle; myosin, heavy polypeptide 9a, non-muscle; myosin-2a; myosin9; Myosin-9; myosin-9; myosin-9a; myosin-9-like; NMHC II-A; NMHC-II A; NMHCIIA; NMHC-II-A; NMMHC IIA; NMMHC II-a; nmmhca; NMMHC-A; NMMHC-IIA; non-muscle myosin heavy chain 9; non-muscle myosin heavy chain A; non-muscle myosin heavy chain II A; non-muscle myosin heavy chain IIa; nonmuscle myosin heavy chain II-A; non-muscle myosin heavy polypeptide 9; nonmuscle myosin II heavy chain A; TU72.6; Unknown (protein for IMAGE:7151033); Unknown (protein for IMAGE:7177375); Unknown (protein for IMAGE:7268224); wu:fi22c04; wu:fi22c04 protein; wu:fj85e11; XELAEV_18023533mg; zgc:162029; zgc:66164; zNMHC-IIA | |
| Rabbit | |
| Sequential chromatography | |
| RUO | |
| 100911597, 17886, 4627 | |
| -20°C | |
| Liquid |
| Western Blot, Immunocytochemistry | |
| 1 mg/mL | |
| PBS with 50% glycerol and 0.02% sodium azide; pH 7.4 | |
| P35579, Q62812, Q8VDD5 | |
| MYH9 | |
| A synthesized peptide derived from human MYH9(Accession P35579), corresponding to amino acid residues around phosphorylated Ser1943. | |
| 100 μL | |
| Primary | |
| Human, Mouse, Rat | |
| Antibody | |
| IgG |
Product Content Correction
Your input is important to us. Please complete this form to provide feedback related to the content on this product.
Product Title
Spot an opportunity for improvement?Share a Content Correction