Learn More
Invitrogen™ PSMA1 Polyclonal Antibody
Rabbit Polyclonal Antibody
Supplier: Invitrogen™ PA1963
Description
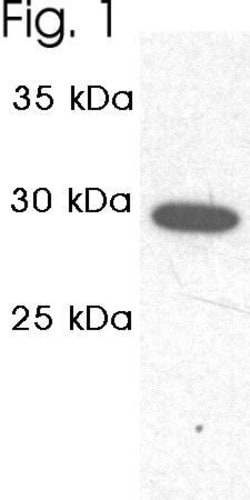
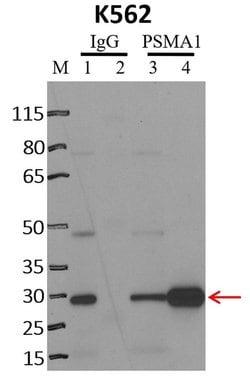
PA1-963 detects proteasome 20S C2 subunit from canine, hamster, human, mouse and rat tissues and cells. PA1-963 has been successfully used in Western blot procedures. By Western blot, this antibody detects a 29 kDa protein representing proteasome 20S C2 subunit from rat brain extract. PA1-963 immunizing peptide corresponds to amino acid residues 249-263 from the C-terminus of human proteasome 20S C2 subunit. This sequence is 93% conserved in the rat and chicken protein and 87% conserved in the mouse protein. PA1-963 immunizing peptide (Cat. # PEP-100) is available for use in neutralization and control experiments.
Proteolytic degradation is critical to the maintenance of appropriate levels of short-lived and regulatory proteins as important and diverse as those involved in cellular metabolism, heat shock and stress response, antigen presentation, modulation of cell surface receptors and ion channels, cell cycle regulation, transcription, and signaling factors. The ubiquitin-proteasome pathway deconstructs most proteins in the eukaryotic cell cytosol and nucleus. Others are degraded via the vacuolar pathway which includes endosomes, lysosomes, and the endoplasmic reticulum. The 26S proteasome is an ATP-dependent, multisubunit (approximately31), barrel-shaped molecular machine with an apparent molecular weight of approximately2. 5 MDa. It consists of a 20S proteolytic core complex which is crowned at one or both ends by 19S regulatory subunit complexes. The 19S regulatory subunits recognize ubiquitinated proteins and play an essential role in unfolding and translocating targets into the lumen of the 20S subunit. An enzymatic cascade is responsible for the attachment of multiple ubiquitin molecules to lysine residues of proteins targeted for degradation. Several genetic diseases are associated with defects in the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway. Some examples of affected proteins include those linked to cystic fibrosis, Angelman's syndrome, and Liddle syndrome.
Specifications
| PSMA1 | |
| Polyclonal | |
| Unconjugated | |
| PSMA1 | |
| 20S proteasome subunit C2; 30 kDa prosomal protein; alpha-type; C2; epididymis secretory protein Li 275; HC2; HEL-S-275; macropain subunit C2; macropain subunit nu; MGC14542; MGC14575; MGC14751; MGC1667; MGC21459; MGC22853; MGC23915; multicatalytic endopeptidase complex subunit C2; NU; PROS30; PROS-30; proteasome (prosome, macropain) subunit, alpha type 1; proteasome (prosome, macropain) subunit, alpha type, 1; proteasome 20S subunit alpha 1; proteasome alpha 1 subunit; proteasome component C2; Proteasome nu chain; proteasome subunit alpha 1; Proteasome subunit alpha type-1; proteasome subunit nu; proteasome subunit, alpha-type, 1; protein P30-33K; PSC2; Psma1; testicular tissue protein Li 150 | |
| Rabbit | |
| Antigen affinity chromatography | |
| RUO | |
| 100773907, 26440, 29668, 476867, 5682 | |
| -20°C, Avoid Freeze/Thaw Cycles | |
| Liquid |
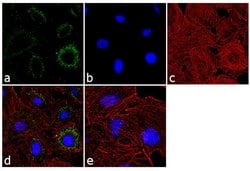
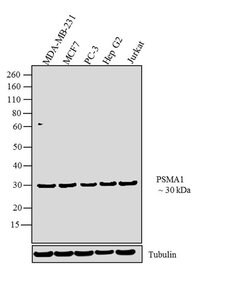
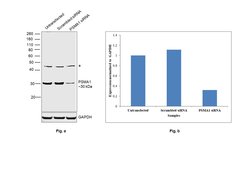
| Immunoprecipitation, Western Blot, RNA Immunoprecipitation, Immunocytochemistry | |
| 1 mg/mL | |
| PBS with 1mg/mL BSA and 0.05% sodium azide | |
| P18420, P25786, Q9R1P4 | |
| PSMA1 | |
| Synthetic Peptide: C P(249) A D E P A E K A D E P M E H(263). | |
| 100 μg | |
| Primary | |
| Human, Mouse, Rat, Canine, Hamster | |
| Antibody | |
| IgG |
Your input is important to us. Please complete this form to provide feedback related to the content on this product.