Learn More
Invitrogen™ WISP2 Polyclonal Antibody, Biotin, PeproTech®, Invitrogen™
Rabbit Polyclonal Antibody
Supplier: Invitrogen™ 500P212BT25UG

Description
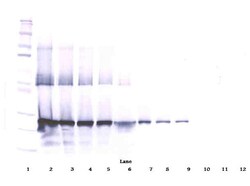
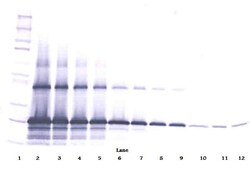
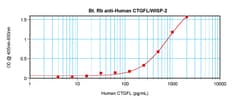
AA Sequence of recombinant protein: MQLCPTPCTC PWPPPRCPLG VPLVLDGCGC CRVCARRLGE PCDQLHVCDA SQGLVCQPGA GPGGRGALCL LAEDDSSCEV NGRLYREGET FQPHCSIRCR CEDGGFTCVP LCSEDVRLPS WDCPHPRRVE VLGKCCPEWV CGQGGGLGTQ PLPAQGPQFS GLVSSLPPGV PCPEWSTAWG PCSTTCGLGM ATRVSNQNRF CRLETQRRLC LSRPCPPSRG RSPQNSAF. Preparation: Produced from sera of rabbits immunized with highly pure Recombinant Human CTGFL/WISP-2. Anti-Human CTGFL/WISP-2-specific antibody was purified by affinity chromatography and then biotinylated. Sandwich ELISA: To detect hCTGFL/WISP-2 by sandwich ELISA (using 100 μL/well antibody solution) a concentration of 0.25-1.0 μg/mL of this antibody is required. This biotinylated polyclonal antibody, in conjunction with PeproTech Polyclonal Anti-Human CTGFL/WISP-2 (500-P212) as a capture antibody, allows the detection of at least 0.2-0.4 ng/well of Recombinant hCTGFL/WISP-2. Western Blot: To detect hCTGFL/WISP-2 by Western Blot analysis this antibody can be used at a concentration of 0.1-0.2 μg/mL. Used in conjunction with compatible secondary reagents the detection limit for Recombinant hCTGFL/WISP-2 is 1.5-3.0 ng/lane, under either reducing or non-reducing conditions. 500-P212BT-1MG will be provided as 2 x 500 μg
Wisp2 a member of the WNT1 inducible signaling pathway (WISP) protein subfamily, which belongs to the connective tissue growth factor (CTGF) family. WNT1 is a member of a family of cysteine-rich, glycosylated signaling proteins that mediate diverse developmental processes. The CTGF family members are characterized by four conserved cysteine-rich domains: insulin-like growth factor-binding domain, von Willebrand factor type C module, thrombospondin domain and C-terminal cystine knot-like (CT) domain. Wisp2 lacks the CT domain which is implicated in dimerization and heparin binding. It is 72% identical to the mouse protein at the amino acid level. This gene may be downstream in the WNT1 signaling pathway that is relevant to malignant transformation. Its expression in colon tumors is reduced while the other two WISP members are overexpressed in colon tumors. It is expressed at high levels in bone tissue, and may play an important role in modulating bone turnover.
Specifications
| WISP2 | |
| Polyclonal | |
| Biotin | |
| CCN5 | |
| CCN family member 5; CCN family protein COP-1; Ccn5; connective tissue growth factor-like protein; Connective tissue growth factor-related protein 58; Cop1; Crgr4; CT58; CTGFL; CTGF-L; Rcop1; UNQ228/PRO261; WISP2; WISP-2; WNT1 inducible signaling pathway protein 2; WNT1-inducible-signaling pathway protein 2 | |
| Rabbit | |
| Antigen affinity chromatography | |
| RUO | |
| 8839 | |
| -20°C | |
| Lyophilized |
| ELISA, Western Blot | |
| 0.1-1.0 mg/mL | |
| PBS with no preservative | |
| O76076 | |
| CCN5 | |
| E.coli-derived Recombinant Human CTGFL/WISP-2. | |
| 25 μg | |
| Primary | |
| Human | |
| Antibody |
The Fisher Scientific Encompass Program offers items which are not part of our distribution portfolio. These products typically do not have pictures or detailed descriptions. However, we are committed to improving your shopping experience. Please use the form below to provide feedback related to the content on this product.