Learn More
Lck with control Mouse anti-Human, Unlabeled, Clone: MOL 171, BD
Mouse Monoclonal Antibody
Specifications
| Antigen | Lck with control |
|---|---|
| Clone | MOL 171 |
| Applications | Immunoprecipitation, Western Blot |
| Classification | Monoclonal |
| Conjugate | Unconjugated |
| Catalog Number | Mfr. No. | Quantity | Price | Quantity & Availability | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Catalog Number | Mfr. No. | Quantity | Price | Quantity & Availability | |||||
|
BDB551047
|
BD Biosciences
551047 |
50 μg | N/A | N/A | N/A | ||||
Description
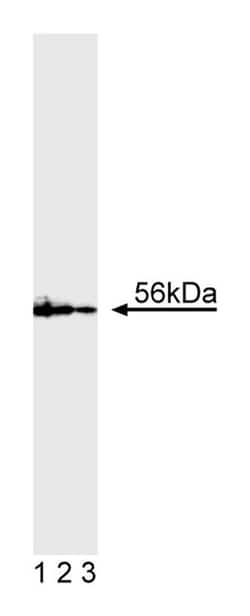
The T-cell receptor (TCR) is a multi-chain transmembrane receptor responsible for antigen recognition on the T-cell surface. T cells also express several other integral membrane proteins, including CD4 and CD8, which play significant roles in the functional responses of the TCR to antigen presentation. Following antigen or ligand binding to the TCR, a series of interrelated membrane and cytoplasmic activation or signaling events rapidly occurs. These events include tyrosine phosphorylation of membrane and cytoplasmic proteins, plasma membrane inositol phospholipid hydrolysis, increases in cytoplasmic calcium concentrations, and increases in protein kinase C activity. The earliest measurable biochemical changes are the appearance of newly phosphorylated tyrosine residues on a variety of cytoplasmic and membrane proteins. Phosphorylation of tyrosine residues is mediated by protein tyrosine kinases (PTKs). Several different PTKs have been implicated in early phosphorylation events of T cell activation, including lck. p56-lck is a member of the Src family, and its functional domains can be divided into two regions based on sequence comparison with p60-src. The N-terminal half, which is highly divergent, contains the membrane bound/substrate interactive domain. The C-terminal half, which has more conserved homology, contains the kinase domain. Lck is normally expressed exclusively in cells of lymphoid lineage, primarily T cells, and natural killer cells. Lck is generally expressed at detectable levels in T-cell lines, including CTLL-2 (ATCC TIB-214) and Jurkat. Lower levels of lck expression have been detected in B cells. Aberrant expression of lck has been described in human colon and lung carcinoma cell lines. Lck plays a role T-cell signal transduction through its physical association with the cytoplasmic tails of CD4 and CD8 expressed in helper and cytolytic T-cells, respectively. The importance of lck in T cell activation is supported by genetic studies. For example, mice with lck null mutations lack T cell development. Additionally, mice expressing only mutant CD4 that is unable to bind to lck, lack the ability to activate T cells through the TCR. MOL 171 reacts with human lck proteins (56-60 kDa). It cross-reacts with mouse lck proteins. A 25 amino acid synthetic peptide corresponding to the N-terminal region of the human lck sequence was used as immunogen.
Specifications
| Lck with control | |
| Immunoprecipitation, Western Blot | |
| Unconjugated | |
| RUO | |
| Human N-terminal Lck | |
| Primary |
| MOL 171 | |
| Monoclonal | |
| Mouse | |
| Human, Mouse | |
| IgG1 κ | |
| Affinity Purified |
For Research Use Only.
Your input is important to us. Please complete this form to provide feedback related to the content on this product.