Learn More
MP Biomedicals™ β-Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide, Oxidized Form, MP Biomedicals™
Shop All MP Biomedicals, Inc ProductsDescription
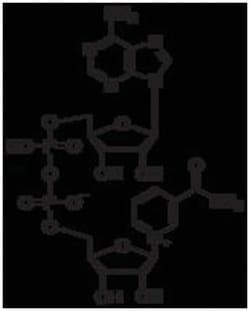
β-NAD, a pyridine nucleotide and biologically active form of nicotinic acid, is a coenzyme necessary for the catalytic reaction of certain enzymes. It occurs in living cells primarily in the oxidized state. It serves as a coenzyme of the dehydrogenases, especially in the dehydrogenation of primary and secondary alcohols. NAD usually acts as a hydrogen acceptor, forming NADH which then serves as a hydrogen donor in the respiratory chain.
- Electron acceptor.
- β-NAD is a carrier for the hydride ion, forming b-NADH.
- Hydride ion is enzymatically removed from a substrate molecule by the action of dehydrogenases such as malic dehydrogenase and lactic dehydrogenase.
- Such enzymes catalyze the reversible transfer of a hydride ion from malate or lactate to b-NAD to form the reduced product, b-NADH.
- Unlike b-NAD which has no absorbance at 340nm, b-NADH absorbs at 340nm (EmM = 6.22).
- The increase in absorbance at 340nm with the formation of b-NADH is the basis for measurement of activity of many enzymes.

Specifications
Specifications
| Grade | Cell Culture |
| Purity | ≥98% |
| pH | 2 to 4 (1% aq soln) |
| Content And Storage | 0°C, Desiccate |
| Quantity | 500 mg |
| Molecular Weight (g/mol) | 663.4 (anhyd.) |
Safety and Handling
By clicking Submit, you acknowledge that you may be contacted by Fisher Scientific in regards to the feedback you have provided in this form. We will not share your information for any other purposes. All contact information provided shall also be maintained in accordance with our Privacy Policy.